Niacinamide is one of the most demanding active ingredients in current trends. It exists literally in every skincare product; becoming the star ingredient in serums, moisturizers, and cleansers. You might be wondering, why is it everywhere?
Niacinamide is a friend that everyone wishes to have in the skincare world. Being a multi-tasking compound, it could fit in with other active ingredients and compromise each other very well to boost your skin.
If you aren’t quite sure what Niacinamide is or what it’s doing to your skin, you’re not alone. Here’s almost everything you should know about Niacinamide and why it’s such a star.
The History of Niacinamide
Niacinamide, which is also called nicotinamide, is a derivative form of Vitamin B3 (Niacin). This kind of vitamin is generally found in a variety of dietary sources including poultry, legumes, and eggs. It is almost everything that you eat and as such, deficiencies of this vitamin aren’t common. However, you may be wondering, what may happen to you if you lack Vitamin B3?

Several countries in the past which were insufficient in food resources had to face a disease due to the deficiency of Vitamin B3, known as Pellagra. Pellagra includes the triad of dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhoea as well as may result in death.
In the year 1937, an American biochemist named Conrad Arnold Elvehjem discovered Niacin and its derivatives can treat Pellagra. His discovery was based on the extensive studies of Dr Joseph Goldberger, a physician in the U.S. government's Hygienic Laboratory. He was the person who revealed the true nature of this disease.
At present, with the improvement in our lifestyle and diet; Pellagra can be termed as the “forgotten entity” with just several cases reported per year.
Is Niacinamide Effective in Skincare?
Scientists theorize that Niacinamide may be effective in skincare products because it’s a precursor to two important co-enzymes within our cells; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+/NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+).

Both of these molecules are central to the chemical reactions that your skin cells need to repair the damage, reproduce themselves, and function normally. Many of these essential reactions can’t occur at all without NAD+, which your cells can’t make without Niacinamide. In simpler words, help your body create more NAD+ which is essential in repairing your skin’s damage.
There’s also evidence that topical Niacinamide can increase the production of Ceramides, the lipids that help maintain the skin’s protective barrier. Hence, it may contribute to its topical effects on wrinkles, fine lines, and the skin’s moisture barrier.
What is The Best Concentration for Niacinamide?
Since Niacinamide is beneficial to the skin, should you buy the topical Niacinamide with the highest concentration?
One thing you should bear in mind when it comes to skincare is that a higher percentage does not increase the effectiveness of your skin.
Imagine eating your favourite food, will you eat your meal more than usual? Surely you will, but overconsumption of your favourite meal can make you feel bloated and lethargic.
It is the same situation for your skin. A higher percentage of Niacinamide might irritate you if you have sensitive skin as there’s no reliable evidence that higher percentages work better.
A Lower Concentration of Niacinamide Can Do Majors on Skin
However, here are a few studies that could prove to you that this star ingredient works amazingly even at lower concentrations.
2% Niacinamide
- Reduces Sebum Production - 50 subjects who applied 2% Niacinamide moisturizer to the face for 4 weeks had lower sebum secretion than 50 subjects who applied placebo moisturizer.
- Strengthens Barrier Function - The forearms of 46 subjects treated with 2% Niacinamide twice daily for 4 weeks had better barrier function and were significantly more hydrated than the non-treated, control forearms.

- Lightens Skin Tone - 120 subjects with facial tanning treated with 2% Niacinamide + sunscreen for 4 weeks had achieved lighter skin tone compared to the placebo group.
4% Niacinamide
Alleviates Acne Breakouts - 38 subjects with mild to moderate acne vulgaris had decreased number of comedones, pustules and papules at the end of the 8-week treatment with a 4% Niacinamide gel which was applied twice daily.

Improves Brown Patches / Freckles - 27 subjects had one side of the face treated with 4% Niacinamide cream and another side treated with 4% Hydroquinone cream which is a gold-standard drug for hyperpigmentation. The result shows that 44% improvement was observed on the side treated with Niacinamide vs 55% improvement with Hydroquinone.
Reduces Wrinkles - One side of the eye area of 29 subjects treated with 4% Niacinamide for 8 weeks had reduced wrinkle grades compared to the other side of the eye area treated with a product without Niacinamide.
5% Niacinamide
Prevents Signs of Aging - Half of the faces of 50 subjects treated with 5% Niacinamide showed significant reductions in fine lines, wrinkles, brown spots, red blotchiness and skin yellowing than the other half of the untreated face.
Lessen Pigmented Spots - 18 subjects treated with 5% Niacinamide had a reduction in graded visible spot pigmentation at 8 weeks compared with vehicle control.
Niacinamide Products at the Safest Concentration
With the principle of “less Niacinamide can be more”, we are proud to suggest to you a few of the best products of this star ingredient.
Paula's Choice SKIN BALANCING Pore-Reducing Toner is a lightly hydrating toner that regulates oily skin and minimizes pores while its potent antioxidants, anti-irritants and cell-communicating ingredients go to work to restore and repair damaged skin.
It would be an ideal option for those with normal to oily or combination skin who are also struggling with enlarged pores, blemishes, bumps, and dry flaky areas of skin.

Garden of Wisdom Niacinamide Serum hits the sweet spot of including an ideal 5% concentration of Niacinamide in this serum, consistent use of this multitasking formula erases many skin concerns at once, creating perfect, youthful skin with a soft glow. This serum is ideal for all skin types; especially anyone with enlarged pores, breakouts, blackheads and uneven skin tone.

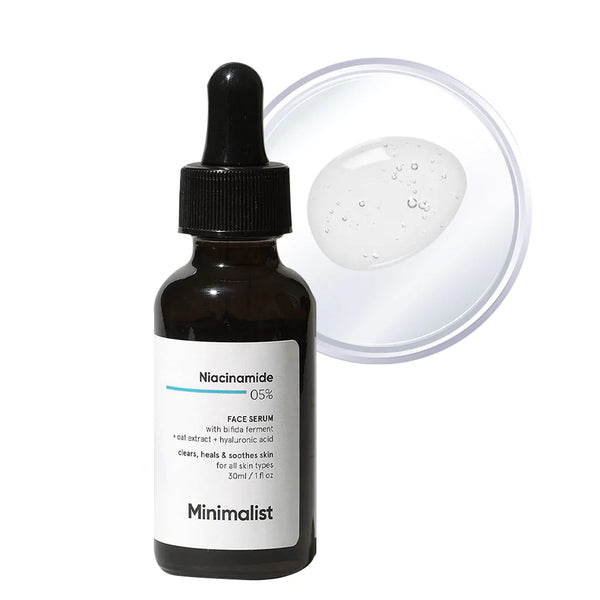
Minimalist Niacinamide 5% + Hyaluronic Acid 1% is a lightweight nourishing and hydrating daily serum. It is the one which will repair and soothes sensitive skin which is ideal for people with dry and sensitive skin. Also, it is perfect for those who find Niacinamide 10% a little strong.
Have you tried any of the suggested products above? Hope to hear your personal experience with Niacinamide in the comment section below! :)
References:
Bissett, D.L., Miyamoto, K., Sun, P., Li, J. and Berge, C.A. (2004), Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in ageing facial skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 26: 231-238. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2494.2004.00228.x
Brahmaiah, U., Parveda, A. R., Hemalatha, R., & Laxmaiah, A. (2019). Pellagra: A forgotten entity. Clinical Dermatology Review, 3(2), 126.
Draelos, Z. D., Ertel, K., & Berge, C. (2005). Niacinamide-containing facial moisturizer improves skin barrier and benefits subjects with rosacea. CUTIS-NEW YORK-, 76(2), 135.
Draelos, Z. D., Matsubara, A., & Smiles, K. (2006). The effect of 2% niacinamide on facial sebum production. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 8(2), 96-101.
Hakozaki, T., Minwalla, L., Zhuang, J., Chhoa, M., Matsubara, A., Miyamoto, K., ... & Boissy, R. E. (2002). The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. British Journal of Dermatology, 147(1), 20-31
Josefina Navarrete-Solís, Juan Pablo Castanedo-Cázares, Bertha Torres-Álvarez, Cuauhtemoc Oros-Ovalle, Cornelia Fuentes-Ahumada, Francisco Javier González, Juan David Martínez-Ramírez, Benjamin Moncada, "A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma", Dermatology Research and Practice, vol. 2011, Article ID 379173, 5 pages, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/379173.
Kawada, A., Konishi, N., Oiso, N., Kawara, S., & Date, A. (2008). Evaluation of anti‐wrinkle effects of a novel cosmetic containing niacinamide. The Journal of dermatology, 35(10), 637-642.
Kaymak, Y., & Onder, M. (2008). An investigation of efficacy of topical niacinamide for the treatment of mild and moderate acne vulgaris. J Turk Acad Dermatol, 2(4), jtad82402a.
Morabia, A. (2008). Joseph Goldberger's research on the prevention of pellagra. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 101(11),566-568.
Reduces Sebum Production
Tanno, O., Ota, Y., Kitamura, N., Katsube, T., & Inoue, S. (2000). Nicotinamide increases biosynthesis of ceramides as well as other stratum corneum lipids to improve the epidermal permeability barrier. The British journal of dermatology, 143(3), 524–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2000.03705.x


